CRM software with GDPR compliance features is crucial for businesses handling personal data. Understanding and implementing GDPR compliance within your CRM system is not just about avoiding hefty fines; it’s about building trust with your customers and establishing a robust data protection framework. This ensures ethical data handling, strengthens your brand reputation, and fosters a culture of responsible data management.
This exploration delves into the essential features of GDPR-compliant CRM software, highlighting data security measures, consent management, and cross-border data transfer protocols. We’ll examine data minimization strategies, retention policies, and the importance of employee training, ultimately guiding you towards selecting and utilizing a compliant system effectively.
GDPR Compliance in CRM Software
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significantly impacted how businesses handle personal data. For organizations utilizing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, understanding and implementing GDPR compliance is crucial. This article delves into the key aspects of GDPR compliance within CRM software, covering essential features, security measures, and best practices for data handling.
Introduction to GDPR Compliance in CRM Software
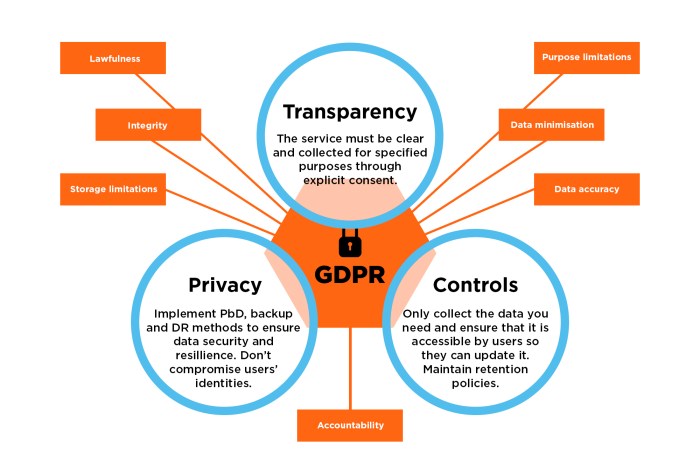
GDPR’s core tenets relevant to CRM data handling center around data protection by design and default, lawful basis for processing, data subject rights, and accountability. Businesses must ensure they have a lawful basis (consent, contract, legal obligation, etc.) for processing any personal data stored in their CRM. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
Conversely, adhering to GDPR fosters trust, strengthens brand reputation, and provides a competitive advantage.
Key Features of GDPR-Compliant CRM Software
Several key features are essential in a GDPR-compliant CRM. These features ensure data protection, facilitate data subject rights, and simplify compliance efforts.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Transforms data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access. | Enhanced data security, preventing breaches and data loss. | Using AES-256 encryption to protect customer data at rest and in transit. |
| Access Control & User Roles | Defines specific permissions for different user roles, limiting access to sensitive data based on job responsibilities. | Minimizes the risk of data exposure by restricting access to authorized personnel only. | Sales representatives only having access to customer contact information, while managers can access all data. |
| Data Subject Access Requests (DSAR) Management | Streamlines the process of fulfilling data subject access requests, allowing users to easily access, correct, or delete their data. | Ensures efficient compliance with data subject rights, minimizing processing time and resources. | Automated system for generating reports of personal data held on a user upon request. |
| Consent Management | Provides tools to obtain, document, and manage user consent for data processing. | Demonstrates lawful basis for data processing, simplifying audits and compliance checks. | A clear opt-in checkbox for marketing communications within the CRM system. |
| Auditing & Logging | Records all data access and modifications, providing an audit trail for compliance and investigation purposes. | Supports accountability by tracking data access and modifications, assisting with data breach investigations. | Detailed logs of who accessed, modified, or deleted specific data records. |
Data encryption, both at rest and in transit, is paramount. Anonymization techniques, like data masking, further enhance security by removing identifying information while retaining data usability for analysis. DSARs are crucial; a compliant CRM should automate the process of fulfilling these requests, minimizing manual effort and ensuring timely responses.
Data Security Measures in GDPR-Compliant CRM
Robust data security measures are critical for GDPR compliance. These measures help prevent data breaches and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal data.
- Data Encryption: Using strong encryption algorithms (like AES-256) to protect data both at rest and in transit.
- Access Control: Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security controls.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploying IDPS to monitor network traffic and detect malicious activities.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implementing DLP measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
Symmetric encryption (like AES) is faster but requires secure key exchange, while asymmetric encryption (like RSA) offers stronger key management but is slower. The choice depends on specific needs and security requirements. A hypothetical data breach response plan would involve immediate containment, investigation, notification of authorities and affected individuals, and remediation.
Consent Management and User Preferences
Obtaining and documenting explicit, informed consent is vital. Preference centers empower users to control their data, enhancing transparency and trust. Clear, concise privacy policies, easily accessible within the CRM interface, are crucial.
Best practices include using clear and unambiguous language in consent forms, providing granular control over data usage preferences, and offering an easy way for users to withdraw their consent at any time.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Data minimization involves collecting and processing only the minimum amount of personal data necessary for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Purpose limitation means that data should only be used for the purposes for which it was originally collected.
A data audit involves systematically reviewing all personal data held within the CRM, identifying data that is no longer needed, and securely deleting or anonymizing it. This process should be documented and regularly repeated.
Cross-Border Data Transfers

Transferring personal data across borders requires careful consideration of GDPR’s requirements. Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) are common mechanisms to ensure compliant transfers.
The choice between SCCs and BCRs depends on the specific circumstances of the data transfer. Both mechanisms aim to provide adequate safeguards for personal data.
Data Retention Policies and Procedures
A sample data retention policy should specify the retention period for different categories of personal data, based on legal requirements and business needs. Secure deletion or anonymization procedures should be clearly defined and documented.
Regular review and updates of the data retention policy are essential to ensure ongoing compliance.
Vendor Selection and Due Diligence
Selecting a GDPR-compliant CRM vendor requires careful consideration of several factors. A comprehensive due diligence process should be undertaken to verify the vendor’s compliance with GDPR.
Ongoing monitoring of the vendor’s compliance is crucial to maintain the organization’s own compliance posture.
Employee Training and Awareness, CRM software with GDPR compliance features
Employee training is crucial for ensuring GDPR compliance. A comprehensive training module should cover data protection principles, data handling procedures, and employee responsibilities.
Key responsibilities include understanding data protection principles, adhering to data handling procedures, and reporting any data breaches or security incidents promptly.
Conclusion
Successfully integrating GDPR compliance into your CRM strategy isn’t merely a regulatory exercise; it’s a strategic move that enhances customer trust, mitigates risk, and positions your business as a responsible data steward. By understanding the core tenets of GDPR and implementing the appropriate features and procedures, businesses can leverage the power of CRM while upholding the highest standards of data protection.
This proactive approach ensures long-term sustainability and competitive advantage in today’s data-driven landscape.
Common Queries: CRM Software With GDPR Compliance Features
What happens if my CRM isn’t GDPR compliant?
Non-compliance can lead to significant fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. It also exposes your business to legal challenges.
How can I ensure my data is encrypted within the CRM?
Look for CRMs that offer robust encryption methods, such as AES-256, both in transit and at rest. Verify the vendor’s security certifications and practices.
What is a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR), and how does my CRM handle it?
A DSAR allows individuals to access, rectify, or erase their personal data. A compliant CRM should have a streamlined process for handling these requests efficiently and securely.
How often should I conduct data audits for GDPR compliance?
Regular data audits, ideally annually or more frequently depending on data volume and sensitivity, are crucial to maintain compliance and identify potential vulnerabilities.
